Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-26 Origin: Site









Linear slide blocks are important parts in linear motion systems. These blocks are also called linear guides. They help hold and guide loads so things move smoothly with little friction. In mechanical engineering, linear motion needs these blocks for accuracy and good work. Linear slide blocks come in different types. Some types are pillow slide blocks, machine slides, dovetail slides, and precision slides. The table below lists common slide types and what they mainly do in linear guide systems:
Slide Type | Primary Role(s) |
|---|---|
Pillow Slide Block | Holds loads, guides movement, lowers friction |
Machine Slide | Keeps out debris, helps things move smoothly |
Dovetail Slide | Lets things move smoothly, needs little care |
Advanced Linear Slide | Gives precise movement in many directions, works better |
Linear slides and linear guide systems affect how well things work and last in many fields. Knowing about them helps people choose the right one for their needs.
Linear slide blocks help machines move smoothly and accurately. They use ball bearings or rollers to lower friction.
They can hold heavy things and still move exactly right. This makes them great for many jobs like making things, robots, and medical tools.
Linear slides come in many kinds and materials. This lets people change them to fit different needs and places.
These systems need careful setup and regular care to work well. This helps them last a long time.
Linear slides cost more than some other choices. But their smooth movement, accuracy, and strength often make them a good buy.
Linear slide blocks are also called linear guide blocks or guide carriages. They help things move in a straight line. These blocks hold weight and move along rails. The rails guide the blocks so they move the same way every time.
The main parts of linear slide blocks are:
Ball bearings: Steel balls roll inside the block. They move on curved paths. This rolling makes movement smooth and lowers friction.
Linear guide block: This part holds the bearings. It carries the weight and slides on the rail.
Linear guide rail: The rail is like a track. It keeps the block moving straight and steady.
Grease (lubrication): Grease helps the bearings last longer. It stops rust and lowers friction.
Note: Seals keep dust and dirt out. This helps the block work well in many places.
Linear slide blocks use deep-groove ball bearing ideas. This spreads weight over a bigger area. It makes the block strong and tough. Blocks with rolling parts can carry heavy things and still move smoothly. These blocks are used for jobs that need high accuracy and long life.
Linear slide blocks have recirculating ball bearings. The balls roll in a loop inside the block. This makes friction much lower than sliding. It helps the guides move quietly and need less fixing. Blocks with rolling bearings can carry a lot and move far while staying accurate.
Linear slide blocks come in many types. Each type has special features for different jobs. The table below shows the main types and how they compare:
Type of Linear Slide Block | Bearing Type | Design Features | Load Capacity | Friction | Rigidity | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Dovetail Slides | Plain surface bearings | Dovetail-shaped fit; strong against side loads | Moderate to high | Low (with lubrication) | High | Large machine tools |
Boxway Slides | Plain surface bearings | Square gib; large contact area | Higher than dovetail | Low (with lubrication) | Very high | Heavy load machines |
Sleeve Bearing Slides | Plain surface bearings | Simple, cylindrical design | Light to medium | Moderate | Moderate | Light machinery |
Linear Ball Bushings | Ball bearings | Recirculating balls in bushings | Medium to high | Low | Moderate to high | Compact designs |
Linear Ball Slides | Ball bearings | Runner block with recirculation | Medium to high | Low | Moderate | Precision motion |
Crossed Roller Slides | Roller bearings | Rollers at angles; line contact | Higher than ball slides | Very low | Very high | CNC centers |
Ball Screw Slides | Ball bearings + screw | Ball bearings with power screw | High | Low | High | Precision positioning |
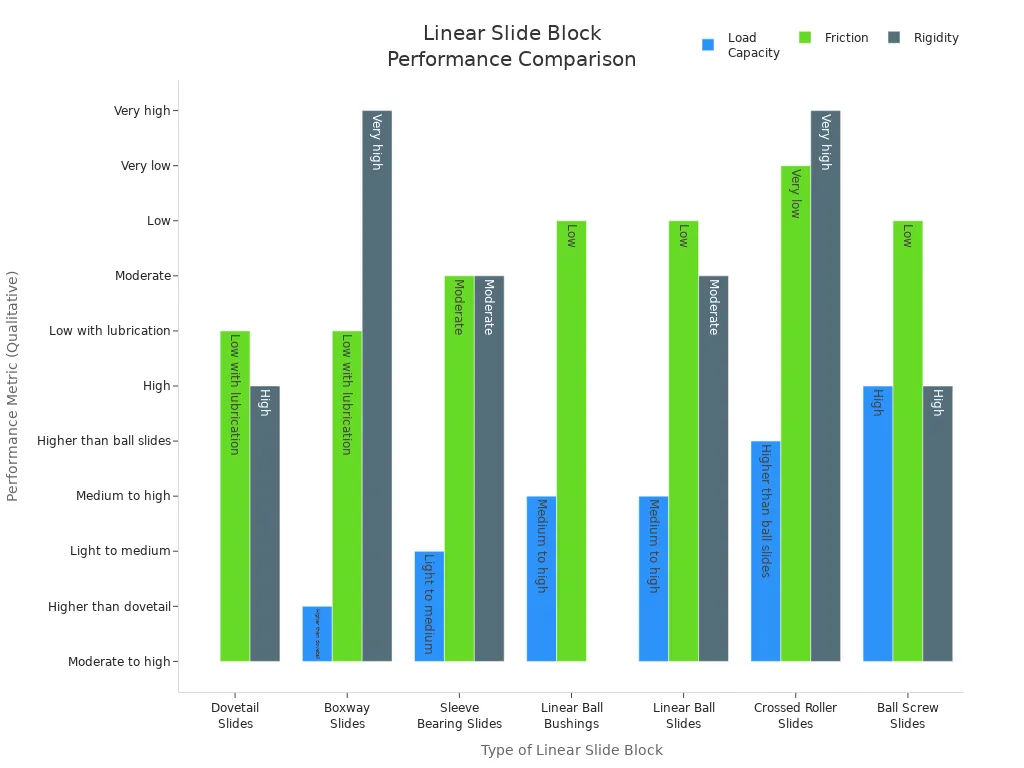
Linear guides are different because of their bearing type and shape. Circular arch raceways make movement smooth and lower friction. Gothic arch raceways let the block carry more weight. Roller bearings give more support and last longer. Some guides use hydrostatic or magnetic bearings for special jobs. These can give very low friction or work at high speeds.
Linear motion slides and guides help many industries move things accurately. Rails and guideways work with blocks to make strong and good guiding systems.
Linear slides help things move very smoothly. This is one of their best features. They use ball bearings or rollers inside the linear guide block. These rolling parts make it easier for things to move. They lower friction a lot compared to old sliding guides. Because of this, linear slides can move fast and quiet. They still work well even when carrying heavy things.
Note: Less friction means the linear guide and bearings last longer.
In fast machines, linear slides with rolling bearings give good control. They help things move the same way every time. Less friction also makes them more accurate. Some linear guide series, like HG, EG, CG, and QH, have special designs. These designs help fix small mistakes during setup. They also keep the motion smooth and steady, even at high speeds.
Series | Key Features | Contribution to Smooth Motion in High-Speed Automation |
|---|---|---|
HG | High load capacity, rigidity, circular-arc groove, self-aligning | Long life, high speed, high accuracy, smooth motion |
EG | Low profile, high load, self-aligning, compact | High-speed, space-saving, accurate, smooth motion |
CG | High moment load, back-to-back bearings, dust protection | Smooth block transition, optimized circulation |
QH | Four-row contact, SynchMotion™ Technology, quiet, long life | Smooth, low-noise, dust-resistant, ideal for automation |
These features work together to lower friction and keep things strong. That is why people pick linear slides for jobs that need smooth and exact movement.
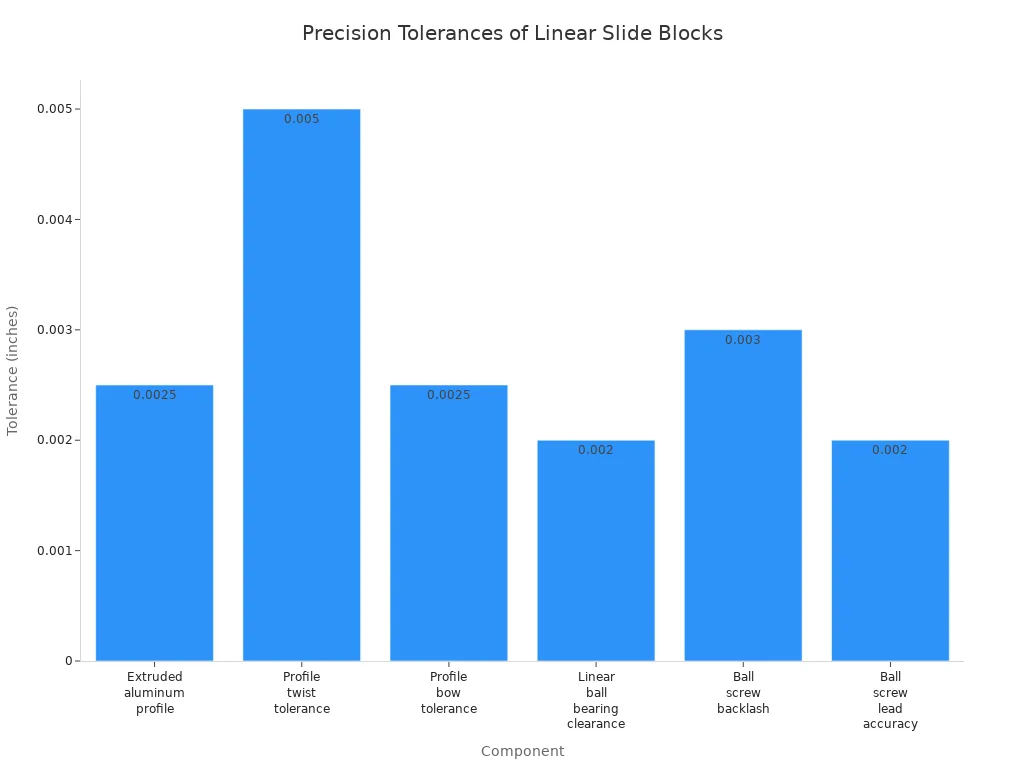
Precision is a big reason people use linear slides. Linear guides use ball bearings or rollers to be very accurate. The rails and bearings are made with tight rules. This helps the block move straight with almost no mistakes.
Accuracy classes set the rules for rail and block size.
Higher accuracy classes are needed for setups with many blocks or rails.
Keeping the rail and block lined up is important for good movement.
Component | Typical Precision Tolerance | Unit |
|---|---|---|
Extruded aluminum profile | ±0.0025 inches (feature size tolerance) | inches (mm) |
Profile twist tolerance | 0.005 inches per 12 inches of stroke | inches (mm) |
Profile bow tolerance | 0.0025 inches | inches (mm) |
Linear ball bearing clearance | ~0.002 inches | inches (mm) |
Ball screw backlash | 0.003 inches | inches (mm) |
Ball screw lead accuracy | 0.002 inches per 12 inches of travel | inches (mm) |
Linear slides are better than plain bearings and dovetail slides for accuracy. Dovetail rails are stable but need careful setup to be precise. Sleeve bearing slides move smoothly but are not as strong or accurate. Linear ball rails use rolling bearings for better accuracy and can carry more weight. They are great for CNC machines, robots, and other jobs where exact movement is needed.
Tip: Air bearing linear slides can be even more precise. But most factories use linear guides with ball or roller bearings. They are a good mix of accuracy, strength, and price.
Linear slides can hold a lot of weight. This is important for many factories. Strong rails and tough bearings let them carry heavy things and still move smoothly. How much they can hold depends on the rail and the bearing.
If the load is heavy and sticks out, it can cause extra stress. Using more bearings or extra supports can help. This lets engineers use smaller slides but still carry big loads. It saves space and keeps things strong and accurate.
Bigger rails can hold more weight but need more room.
Rails with full support bend less and can carry more.
Different ways to hold the load help balance space and strength.
Linear slides with high load capacity are used in making cars, machines, and other big equipment. They help move large parts or tools smoothly and exactly, even when things get tough.
Linear slides are very flexible and can be used in many ways. They work in small labs and big factories. Companies make them in different materials, sizes, and shapes for many needs.
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Materials | Cast iron (strength, rigidity, wear resistance), Aluminum (lightweight, corrosion resistance), Stainless steel (sanitary use) |
Customization | Sizes, load capacities, shaft styles, flange types, seals, lubrication systems |
Types | Motorless (ball bearing, drawer, roller, telescopic), Motorized (XY tables, machine slides, lead screw) |
Features | Low friction, high precision, energy efficiency, easy integration, repeatable motion |
Applications | Robotics, CNC machining, laboratory automation, food processing, medical equipment, semiconductor fabrication, space exploration |
Accessories | Wipers, seals, lubricants, mounting hole caps, clamps, stopper plates, roller tables, height-adjusting blocks |
Advantages | Energy efficiency, minimal maintenance, high load capacity, precision, repeatability, versatility |
You can order linear slides in many sizes and materials. This helps match them to each job. They are strong and do not bend easily. Standard holes make them easy to install. Extras like wipers and seals keep out dust and dirt.
Many industries use linear slides because they are so useful:
Manufacturing: For smooth, precise, and strong movement.
Automotive: Where exact and repeatable moves are needed.
Aerospace: For high precision in complex builds.
Medical device making: For tools that need to be exact and work all the time.
Electronics: For very accurate moves in making chips.
Industrial automation: For moving things in machines and factories.
Note: Linear slides also work well in hot places, with oil systems, and on trains. They last long and do not need much care.
Engineers like linear slides because they can be changed for many jobs. Whether you need exact moves, fast speed, or to carry heavy things, linear slides can do the job.
Linear guide systems usually cost more than other options. Makers use strong steel, stainless steel, or aluminum alloy for rails and blocks. These materials make the price go up. Special coatings like chrome plating or nitriding also add to the cost. Guides with higher accuracy need careful machining and strict checks. Bigger guides and ones that hold more weight need more material and time.
Product Type | Cost Range (USD) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
Roller Linear Guides (IVTAAW series) | $320 - $440 | Aluminum anodized rail, hardened stainless steel races, load capacity up to 8,900 N, speed up to 10 m/s |
Making a custom linear guide from separate parts can cost over $2,000. This price includes ball screws, rails, and bases. Buying a ready-made unit often costs less and needs less fixing. Famous brands charge more for better quality and service.
Profile-rail linear guides need very flat mounting surfaces. This makes installation cost more. Using many rails without planning makes things harder and more expensive. Extras like seals or special grease systems also raise the price.
Plastic linear bearings cost less. They can save up to 40% compared to ball bearing guides. These bearings do not need fixing, grease themselves, and do not rust. They work well in tough places and are quieter.
Factor Category | Description |
|---|---|
Material | High-strength steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy |
Surface Treatment | Chrome plating, nitriding, special coatings |
Accuracy Level | Higher precision grades require complex manufacturing |
Size and Specifications | Larger guides and higher load capacities need more resources |
Brand and Manufacturer | Well-known brands charge more for quality and service |
Production Process | High-precision machining and automation impact cost |
Market Demand | Industry requirements and demand fluctuations affect price |
Accessories and Customization | Extra components and custom features increase cost |
Transportation and Logistics | Distance and packaging requirements add to final price |
Linear guide systems can get dirty easily. Dust, chips, and debris wear out parts and lower accuracy. Dirt makes friction higher and can cause sticking. Water and chemicals can cause rust and make tiny bits. Factories with dust, wet, or harsh chemicals have more risk.
Dust, water, chemicals, and debris are common problems. Bad seals let dirt get inside. Grease can trap dirt or make more bits if used wrong.
Seals, covers, and scrapers help keep dirt out. Stainless steel and PVC fight rust better than plain aluminum or steel. Special coatings and dehumidifiers protect rails in wet places. Cleaning with soft cloths and safe cleaners removes dirt. Do not use strong air blasts because they push dirt into seals.
Dust and dirt inside the guide wear it out faster.
Dirt makes friction higher and can cause sticking.
Dirty grease does not work well and wears out parts faster.
Water and dirt together can cause rust and damage rails.
Looking for marks or pits helps find wear from dirt.
Dust covers or boxes keep dirt out.
Keeping things clean and dry lowers rust risk.
Ball separators stop balls from touching and making bits. Cleanroom grease has fewer solid bits. Mixing greases can break down grease and cause dirt. Special cleaning removes old grease.
Linear guide systems need regular care to work well. Cleaning, greasing, and checking are important. Machines used a lot need more attention. Most guides should get grease every six months or after 100 km. If things are perfect, grease can last up to two years or 500 km. Guides with ball chains may need grease once a year or after 500 km, but it depends on use and place.
Guide Type | Recommended Lubrication Interval (Normal Conditions) | Maximum Interval (Optimal Conditions) | Notes on Adjustment and Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
Conventional Linear Guides (LGBX) | Every 6 months or after 100 km travel | Not longer than 2 years or 500 km travel | Adjust intervals based on load and contamination; use specified grease amounts |
Linear Guides with Ball Chain (LGBG, LGMC) | Once per year or after 500 km travel | Several thousand km possible under good conditions | Adjust intervals based on environment and load; consider lubricant life |
Workers must check guides for strange sounds, rough movement, or more resistance. These signs mean grease is bad or things are not lined up. Regular checks help find rust, leaking grease, dirt, wear, shaking, or noise before big problems happen. Sensors can give alerts using data.
Skipping checks or using wrong grease makes parts wear out faster. It also causes more dirt, friction, noise, and early breakdowns. Not knowing how to care for guides makes them fail sooner.
Cleaning removes dust and dirt. Greasing as the maker says keeps things moving well. Covers protect guides from dirt. Changing old parts as needed makes guides last longer and stops breakdowns.
Putting in linear guide systems can be hard. Everything must be lined up just right. Mounting surfaces must be flat and even. If things are not lined up, friction goes up and parts wear out faster. Not having pins or shoulders for lining up can make movement uneven.
Machining and lining up surfaces must be exact. Bad alignment causes more friction and wear.
Not having features for lining up can make movement uneven.
Wrong preload for the mounting can make things work badly.
Not testing the guide over its whole range can miss problems.
Plates must be flat and parallel. This takes more time and work. Bad installation causes binding and early wear, so parts need changing more often. Dirt during setup can also cause wear or jamming.
Installation Aspect | Linear Guide Systems | Other Linear Motion Technologies |
|---|---|---|
Alignment Sensitivity | Requires precise alignment | More forgiving of misalignment |
Support Structure Requirements | Needs flat, stiff mounting surface | Can be used with less rigid structures |
Linear guide systems need clean, level, and strong bases. Parts must be put in to avoid side loads and bending. The whole setup needs to be stiff and lined up, often checked with special tools. Other systems do not need such careful setup but are less accurate and strong.
Using guides that are too precise for the job costs more and makes things harder. Bigger bearings last longer but make the setup heavier and more expensive.
Engineers must match preload to how well things can be lined up. Testing the guide over its full range helps find problems. Measuring push force makes sure movement is smooth.
Linear slides are used in many industries. They help machines move smoothly and accurately. These guides make movement reliable and safe.
Factories use linear slides for many jobs. Robots and conveyors need linear rails to move exactly. Machine tools also use these rails for good movement. The table below lists common uses and their benefits:
Industrial Automation Application | Description and Usage | Performance Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Robotics (including gantry robots) | Use single or dual rails for exact movement | High precision, repeatable motion, high rigidity |
Automotive Industry Automation | Rails help with assembly and moving parts | Less friction, faster speed, more output |
Linear Actuators | Rails guide fast-moving parts | Can hold heavy loads, smooth motion, reliable |
Overhead Transport Systems | Rails carry heavy things under them | Can hold heavy loads, strong |
Linear Stages | Two rails help with exact placement | Very accurate, little bending |
Machine Tools | Two rails with many blocks | Spreads out the load, better tool quality |
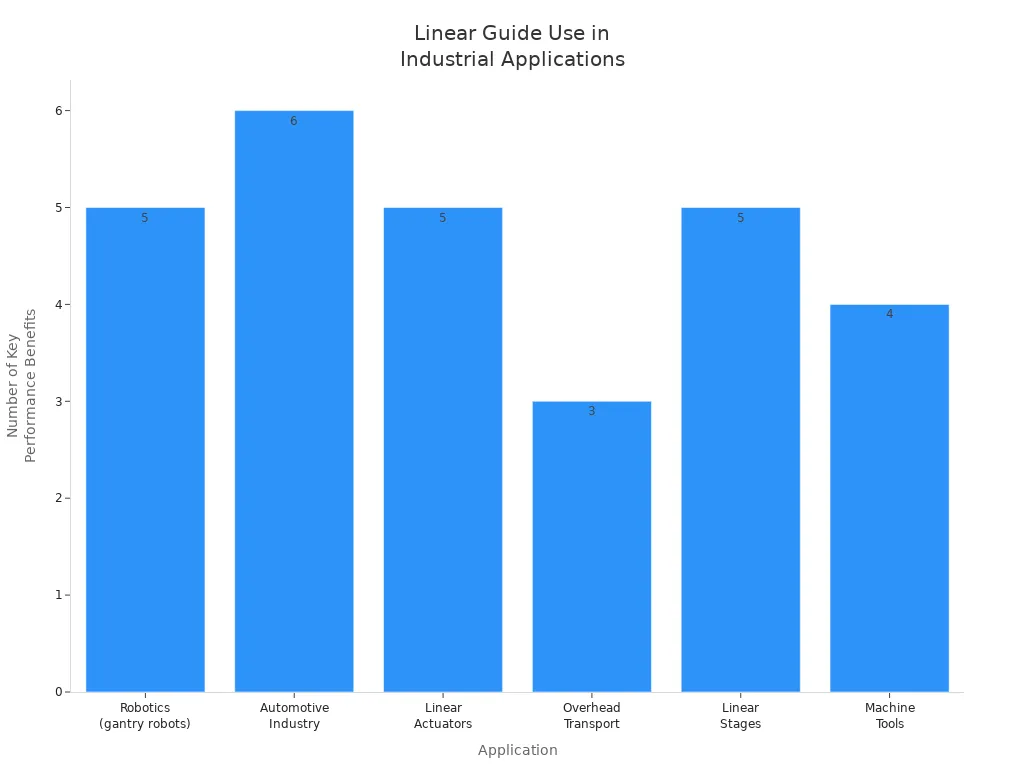
Linear slides help machines move faster and with less friction. They also make machines safer and last longer. But they can cost a lot and need clean places to work well.
CNC machines and 3D printers use linear rails for speed and accuracy. Linear slides help the cutting tool or printer head move straight and fast. This makes sure each part or print is made right.
Linear slides give very exact movement and fast printing.
Built-in rails make machines strong but not heavy.
Less dust means cleaning is easier.
Small designs make machines look better and work well.
Linear guides help CNC tools cut with great accuracy. In 3D printing, they help the nozzle move smoothly for fine details. Dust and dirt can cause problems, so cleaning often is needed. Some cheaper machines use rods and bearings, but linear slides work better for hard jobs.
Robots and medical tools need linear slides for smooth movement. In robots, rails help carry heavy loads and keep movement steady. Medical tools use lighter loads but need quiet and gentle motion for comfort.
Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
High Precision | Needed for robots and medical tools to move exactly. |
Load Capacity | Important for robots; less for medical tools. |
Rigidity | Keeps movement steady and safe. |
Low Friction | Helps things move quietly and smoothly. |
Durability | Materials last longer and resist wear. |
Note: Medical tools often need small, easy-to-clean slides. Designers must think about size, price, and how well they work.
Linear guides in these jobs give smooth and exact movement. But they can be expensive and need careful setup. Picking the right linear slides helps keep things safe, comfortable, and working for a long time.
Linear slide blocks help things move smoothly. They are very accurate and can hold heavy loads. But they cost more money and need careful setup. When picking a linear guide, people should think about these things:
What kind of load and force will be used
How fast and how quickly it will move
How exact the movement needs to be
How often it will be used
How straight and stiff the guide must be
If it needs to do the same thing every time
Anaheim Automation, PBC Linear, and NB Corp. of America have guides and eBooks. These explain how to choose a linear guide. They also give technical facts for engineers and designers.
A linear slide block is a part that moves along a rail. It uses ball bearings or rollers to help things move in a straight line with little friction. Many machines use linear slide blocks for smooth and accurate movement.
A linear slide block bearing uses small steel balls or rollers inside the block. These balls roll along grooves in the rail and block. This rolling action lowers friction and helps the block move smoothly and quietly.
Linear slide blocks come in several types. Common types include linear ball bearing slide blocks, linear bearing slide blocks, and linear motion ball bearing slide blocks. Each type has different load capacities, sizes, and uses in machines.
Regular cleaning and greasing keep a linear bearing slide block working well. Users should check for dirt, rust, or noise. They should follow the maker’s instructions for grease and cleaning. Good care helps the block last longer.
People use linear motion ball bearing slide blocks in CNC machines, 3D printers, robots, and medical tools. These blocks help move parts smoothly and with high accuracy. They work well in places that need strong, repeatable movement.