Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-26 Origin: Site









You can expect linear guide systems with linear slide blocks to hold heavy weights. These linear slide blocks can support loads ranging from hundreds of kilograms up to several tons. The weight capacity of a linear slide block or slide depends on the type of rail used. It also varies based on the size of the block and its intended application. Steel rails paired with linear slide blocks can hold more weight than aluminum rails. While aluminum rails are lighter, they are not as strong. It’s important to know the travel distance your linear guide with linear slide blocks will cover. You should also consider how you will mount the system and the level of accuracy required. This ensures your system remains safe and operates efficiently. When selecting the right linear slide blocks, pay attention to travel distance, block size, and installation method.
Linear slide blocks can hold heavy things. They use strong rails and rolling bearings. These bearings lower friction. This helps the blocks move smoothly.
Steel rails can hold more weight than aluminum rails. Bigger rails with larger balls or rollers carry heavier things. They also stay stiff and do not bend easily.
Ball bearings are good for fast and accurate movement. Roller bearings are better for heavy loads and last longer.
Mounting the rails the right way helps a lot. Using more carriages makes the rails stronger. Rails should be on flat and strong surfaces. This helps them hold more weight and move better.
Taking care of your rails is important. Follow what the maker says. Plan for safety margins. This helps your linear guide last longer and work safely.
Linear slide blocks help machines move in a straight line. They are part of linear guide systems. These blocks help things move smoothly and with accuracy. Linear slide blocks are also called linear motion guides. They have many important parts. The table below lists the main parts and what they do:
Component | Description and Function |
|---|---|
Bearings | Let things move smoothly with little friction; types include ball, roller, plain surface, and magnetic bearings. |
Carriage | Moves on the guide rails, holds the load, and keeps the bearings in place. |
Guide Rails | Give the carriage a straight path to follow for accurate movement. |
End Caps | Cover the ends to keep dust and water out of the inside parts. |
Lubrication Ports | Let you add oil or grease to lower friction and wear. |
Seals | Block dirt and water from getting in and protect the bearings. |
Bellows and Covers | Keep out debris and liquids while still letting the slide move. |
Impact Dampers | Take in shocks and vibrations to protect the slide when it moves fast. |
Control Systems | Electronic parts that control speed, position, and how fast things move in automatic systems. |
Drive Units | Parts that move the carriage, like lead screws, belts, or linear motors. |
Position Sensors | Devices that tell you where the carriage is for better accuracy. |
You can find linear slide blocks in CNC machines, robots, and factory machines. These blocks help things move smoothly and exactly where they need to go.
Linear slide blocks move along a straight guide rail. The carriage holds the weight and slides on bearings. The bearings roll between the carriage and the rail. This makes movement smooth and easy. Ball bearings help things move fast and with accuracy. Roller bearings can hold more weight. The guide rails keep the carriage moving straight. Seals and end caps keep dust and water out. Lubrication ports let you add oil to keep things working well. Control systems and position sensors help with automatic and exact movement. Linear motion guides make sure movement is always smooth and correct.
Tip: When picking a linear guide block, look at the bearing type and the guide rail quality. This helps you get the right weight support and travel accuracy for your job.
Linear slide blocks hold weight by using rolling-element bearings and strong guide rails. Balls or rollers lower friction and help the carriage move easily. Ball bearings touch at one point. This is good for fast movement but not for heavy loads. Roller bearings touch along a line. This lets them hold more weight and last longer. The shape of the raceway, like circular arch or gothic arch, changes how much weight the guide can hold. Circular arch designs have less friction. Gothic arch designs can hold more weight and resist twisting better.
In many factories, people use two linear guides with more than one block. This spreads the weight out and makes the system stiffer. You get better movement and the bearings last longer. The material and shape of the guide rail also change how much weight it can hold. Using linear motion slides gives you smooth movement and strong support.
Rolling-element bearings lower friction and help things move straight.
Ball bearings are best for fast, light jobs.
Roller bearings are better for heavy jobs and last longer.
Two guides and more blocks share the weight for more stability.
The way you set up the bearings, the raceway shape, and the materials all change how much weight can be held.
You should always pick the right linear guide block and rail for your job’s weight and movement needs. This keeps your system safe and working well.
When you pick a linear guide, you need to think about a few things. These things decide how much weight your linear guide can hold and how well it works. You want your system to move with high accuracy, be strong, and last a long time. Let’s look at the main things that change how much weight linear guides can hold.
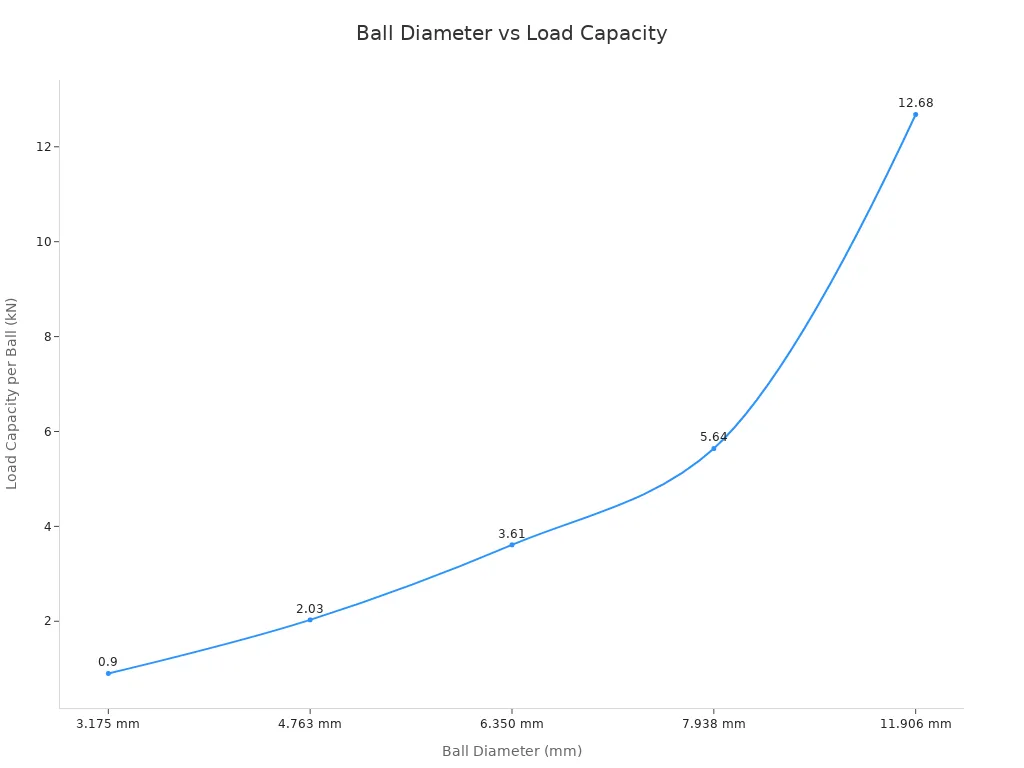
The size of your rail matters a lot for weight support. Bigger rails use larger balls or rollers inside the bearing. Larger balls can carry more weight. You can see this in the table below:
Ball Diameter (mm) | Load Capacity per Ball (R-groove) (kN) |
|---|---|
3.175 | 0.90 |
4.763 | 2.03 |
6.350 | 3.61 |
7.938 | 5.64 |
11.906 | 12.68 |
When ball diameter gets bigger, each ball can hold more weight. This means a bigger rail can carry heavier loads and is stiffer. Some rails have special grooves, like circular-arc grooves. These grooves help each ball hold even more weight. This design gives you very accurate movement and strong rails.
The rail material also matters. Here is a quick comparison:
Material | Mechanical Properties | Effect on Load Capacity |
|---|---|---|
Steel | High strength and durability | Good for heavy loads, high weight support |
Aluminum | Lightweight | Holds less weight than steel |
Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistant | Good for tough places; weight support changes by type |
Steel rails are the strongest and hold the most weight. Aluminum rails are lighter but can’t hold as much. Stainless steel rails work well in wet or dirty places, but their weight support depends on the type. Always match the rail material to your job. If you need to hold a lot of weight and move accurately, steel is usually best.
Tip: Look at ball size and rail material in the specs. Bigger balls and steel rails mean more weight support and better movement.
You should also think about the rail’s shape. Thicker or taller rails bend less. This helps your system stay accurate and steady, even with heavy loads.
The kind of bearing inside your guide block changes how much weight it can hold and how long it lasts. There are two main types: ball bearings and roller bearings.
Caged bearings use a cage to keep balls apart. This makes less noise and helps balls last longer. You get smoother movement and better weight sharing.
Non-caged bearings cost less and work for small loads or slow speeds. They might wear out faster with heavy loads.
Square rails use roller bearings for high weight support and accurate movement. They need careful setup.
Round rails are easier to set up but hold less weight and are less stiff.
Roller bearings can hold about twice as much weight as ball bearings of the same size. They also last longer with heavy loads. Ball bearings give smooth, fast movement and high accuracy. Roller bearings give strong rails and high weight support. If you need very accurate movement, ball bearings are good. If you need to move heavy things, roller bearings are better.
Linear guides with preloaded bearings can hold more weight and stay stiff. Preload means the bearings fit tightly, so there is no loose movement. Too much preload can make your guide wear out faster, so pick the right amount.
Note: Always check bearing type and preload in the specs. Pick roller bearings for heavy loads and ball bearings for accurate movement.
How long your guide lasts depends on the bearing type. Roller bearings last longer with heavy loads. Ball bearings are good for smooth and accurate movement. Both types need good oil and clean rails to work well.
How you set up your rails and the way the weight pushes on them both change weight support and movement accuracy. Linear guides can take weight from different directions, but some ways are better.
Load Direction / Moment Type | Effect on Load Capacity |
|---|---|
Radial Load | Standard rating; highest weight support. |
Reverse Radial Load | Weight support changes; special factors used. |
Lateral Load | Weight support changes; needs special math. |
Pitch Moment | Can tilt; special factor used for real weight. |
Yaw Moment | Sideways twist; changes weight sharing. |
Roll Moment | Turns around rail; changes weight and life. |
Linear guides are best at holding radial loads. If you push from the side or at an angle, weight support drops. Loads that twist, like pitch, yaw, or roll, can make the guide wear out faster. You need to set up your rails the right way to keep movement accurate and steady.
Rails can hold both straight and twisting loads, but always check the load direction for your job.
Preload and clearance help your guide handle loads that tilt or twist.
How you set up the rails changes how the weight pushes on them. Vertical setups often get more twisting loads.
Tip: Always put your rails on a flat, strong surface. Use more than one carriage spaced apart to share the weight and stop twisting. This keeps movement accurate and helps your guide last longer.
Here are some good ways to set up linear guides:
Use rolling bearings to lower friction and help hold weight.
Put more carriages on the rail to spread out the weight and stop twisting.
Make sure your frame is strong and lined up right.
Use encoders for feedback if you need very accurate movement.
Plan for heat and shaking in your design.
Rails with lots of mounting holes are easier to set up and bend less. If you need to cross a gap, use rails instead of shafts for better support.
Remember: How you set up your rails and the way the weight pushes on them both change movement accuracy and weight support. Always follow the maker’s instructions for best results.
If you pay attention to rail size, material, bearing type, and setup, you get a guide system that holds your weight, moves accurately, and lasts a long time. This helps your machines work smoothly and safely.
You must know how much weight your linear guide will hold. First, find the center of gravity for your load. Next, check how far the load sticks out from the slide table. Look at which way the load pushes or twists the slide. These ways are called pitching, yawing, and rolling. Use the load’s mass, gravity, and how far it hangs over to figure out static load moments. When the slide moves, add in acceleration to get dynamic load moments. If you have more than one load, add all the moments together. Compare your answers to the limits in the linear guide’s specs.
Here is an easy example:
Get the dynamic load rating (C) from the maker. For example, C = 1000 N.
Guess the real load (P) on your linear guide. For example, P = 200 N.
Use this formula for life:L = (C / P)^3 × 50
Do the math:L = (1000 / 200)^3 × 50 = 625 kilometers
Choose linear slides that match your life and load needs.
Tip: Always check both static and dynamic loads. Pretend the worst thing happens to make sure your linear guide will last.
You want your linear slides to be safe and last a long time. Safety margins help protect your system from shocks and uneven loads. Use the Design Safety Factor (fs) to compare the rated load to the real load. Change for vibration and bumps with the load factor (fw). Make sure you install everything right and line up the rails. Clean and oil your linear guide often to keep it working well.
Factor | Description | Impact on Reliability |
|---|---|---|
Load Factor (fw) | Changes for vibration and bumps | Stops early failure |
Static Safety Value | Guards against shock loading | Makes it last longer |
Preload | Lowers looseness, makes it stiffer | Helps it last longer |
Proper Installation | Spreads out the load evenly | Stops uneven wear |
Maintenance | Oil and cleaning | Keeps it working well |
Note: Safety margins are not always the same. You must figure them out for your own job. Always plan for extra strength if your system gets shocks or heavy use.
You should always look at the maker’s data before buying linear slides. Check the load capacity, stiffness, and how exact it is. Look at friction and bearing types, like ball bearings or cross-roller bearings. Check the rail design and drive type, like lead screws or ball screws. Make sure the linear guide works in your place, like cleanrooms or hot spots. Makers often give help, testing, and custom choices. These things help you get the best linear guide for your job.
High-load linear slides are good for heavy jobs and keep movement exact.
Special oil systems lower friction and save energy.
Some linear guides work with robots and automatic systems for exact moves.
Things like dust or chemicals can change what you pick.
Makers may give full solutions and help you set things up.
Tip: Always use the maker’s specs to match your load and stiffness needs. If you have a special job, ask about custom choices.
Linear guide systems are used in many industries. They help machines move straight and carry heavy things. You can find linear guides in linear actuators and overhead transport systems. Gantry robots use them to move with accuracy. Machine tools need two linear rails for better movement and strength. Cartesian robots use two rails on each axis for exact moves. Robot transport units use two rails as a “seventh axis” to move robots far. Square linear guides are best for machines and automation because they are strong and smooth. Round linear guides are good for woodworking and moving materials when loads are not too heavy.
Linear actuators help belt, screw, or air-powered systems move.
Overhead transport systems carry heavy things under the rail.
Gantry robots use one rail for accurate moves.
Linear stages use two rails for high accuracy and less bending.
Machine tools need two rails for better movement and to hold more weight.
Cartesian robots use two rails for exact moves.
Robot transport units connect many rails for longer travel.
Tip: Pick the right linear guide for your job. This helps you get the best movement and weight support.
You need to match the load rating to your job. Miniature linear guides are good for small machines. They work well in tight spaces and are very accurate. Heavy-duty roller guides can hold from 11.3 kN up to 275.3 kN. Heavy-duty ball guides can hold from 5.23 kN to 29.8 kN. Some precision linear guides can hold up to 419,000 N, depending on the type and size. Miniature guides are used in chip and science tools. Ball guides are for jobs with lots of weight. Roller guides are best for heavy work in factories.
Linear Guide Type | Series | Basic Dynamic Load Range |
|---|---|---|
Miniature | MG | 0.68 kN - 8.93 kN |
Heavy-Duty Roller | RG | 11.3 kN - 275.3 kN |
Heavy-Duty Ball | WE | 5.23 kN - 29.8 kN |
The place where you use your guide can change how much it can hold. Very hot or cold places can hurt seals and oil. Dust and water can cause rust and make the guide work worse. Use special materials and seals to keep your guide working well.
You can keep your linear guide working well by following good steps. Always check the weight and forces before picking a guide. Use two rails to spread out the weight and make it last longer. Plan your setup and pick one or two rails based on what you need. Put rails on flat, clean surfaces. After you put them in, check if they are lined up for smooth moves.
Use the biggest forces and safety numbers to pick load limits.
Put rails on strong, flat bases with tight measurements.
Use edges and bolts with the right tightness.
Use pins or clamps to keep rails in place.
Check if rails are lined up and straight after putting them in.
Add end seals or scrapers if needed.
Use the right oil and keep up with care.
Check your guide often to find wear, rust, or if it is not straight. Clean the rails and parts to keep things moving smoothly. Sensors can warn you before something breaks. Teach your team and use tags to track care and keep things safe.
Note: Always follow the maker’s steps for putting in and caring for your guide. This helps your guide move well and last a long time.
Picking the right linear slide blocks helps your system stay safe and work well. You need to make sure the load capacity fits your needs. If you do not, your system might wear out early, make noise, or break.
Think about the kind of load, which bearing you use, and how you set up the blocks for the best results.
Follow what the manufacturer says and ask experts if your project is hard or has heavy loads.
Always remember, choosing the right size and putting it in the right way stops problems and helps your linear slide block bearing system last longer.
A linear slide block lets you move loads in a straight line with high accuracy. You use it in machines, robots, and automation systems. You can find many types at Weikente for different weight and precision needs.
You check your load weight, travel distance, and mounting method. You pick a linear slide block bearing that matches your job. You compare ball and roller types for speed or heavy loads. You always use manufacturer data from Weikente for best results.
You can use a linear ball bearing slide block for light to medium loads. You get smooth movement and high accuracy. For very heavy loads, you switch to a linear bearing slide block with rollers. You find both types at Weikente.
You clean and lubricate your linear motion ball bearing slide block every few months. You check for dirt, wear, and alignment. You follow Weikente’s care tips to keep your linear slide block working well and lasting longer.
You affect lifespan by load weight, installation, and maintenance. You use proper mounting and regular lubrication. You avoid overloads and shocks. You check Weikente’s product guides for tips to extend the life of your linear slide block.